The converted data file is now in an X-Y ASCII format that can be directly imported into a number of software programs for continued processing, but most programs will require some manipulation of the file format to make full use of the data. A very useful program for such manipulation is Convert. Information about Convert may be found at:
http://www.ccp14.ac.uk/solution/powderdataconv/index.html
Note: Other programs mentioned here may be found at the CCP14 Homepage
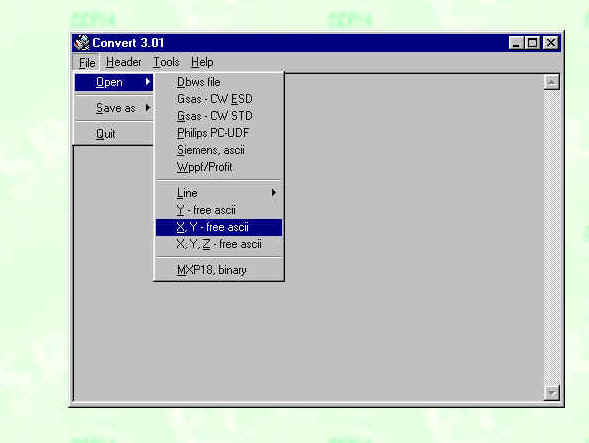
Open the data file:

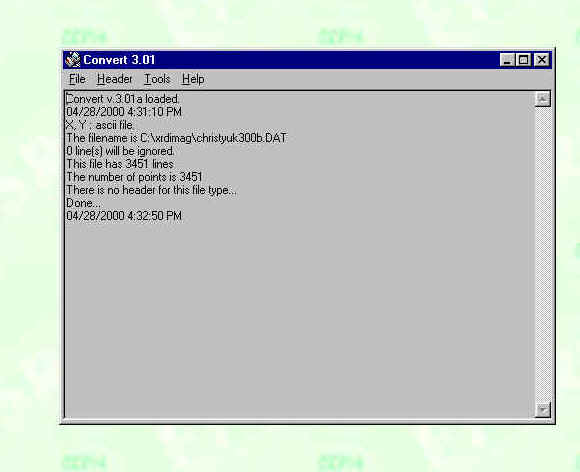
Convert will tell you the data is loaded and the number of data points.
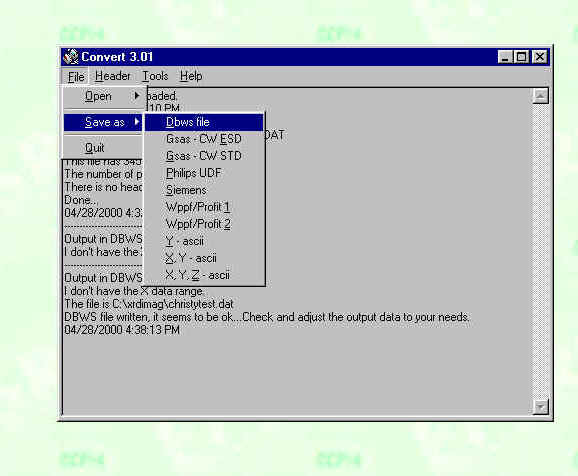
Two formats are generally all you will need, an 8 row format (DBWS) or a 10 row format (GSAS). You can look at a sample file for your program to determine which format is used and what header information is needed. I'll comment on the various types in the section giving examples of various programs. In Convert, save your file (in this example, as a DBWS file):
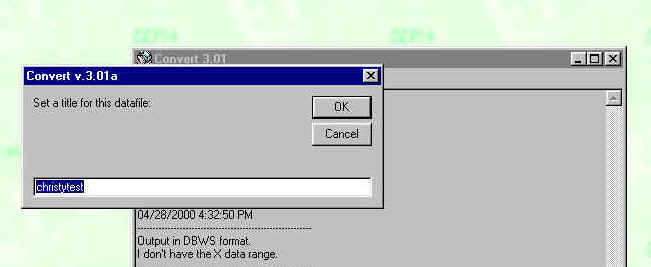
Convert will ask you for a title:
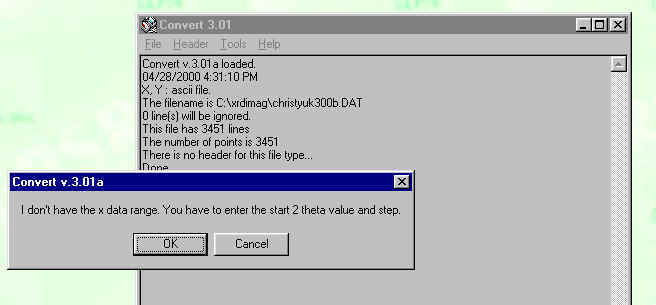
It will then let you know that more information is needed:
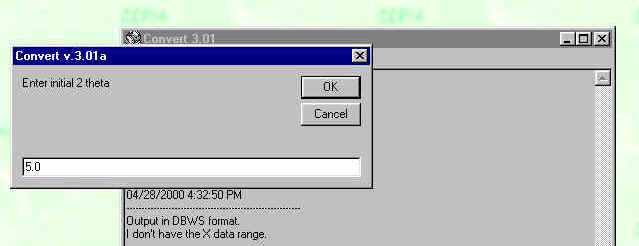
And will ask you for the starting point of the data, in this case 5.0 degree two theta:
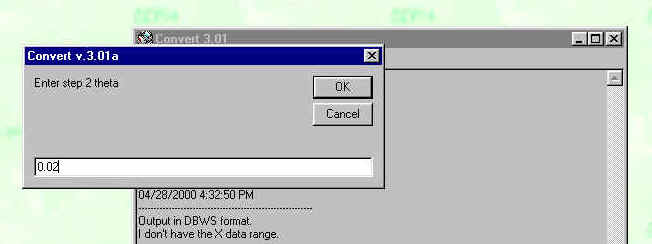
And the step size, in this case 0.02 degrees two theta:
Convert will then save the file. The saved data looks like this:
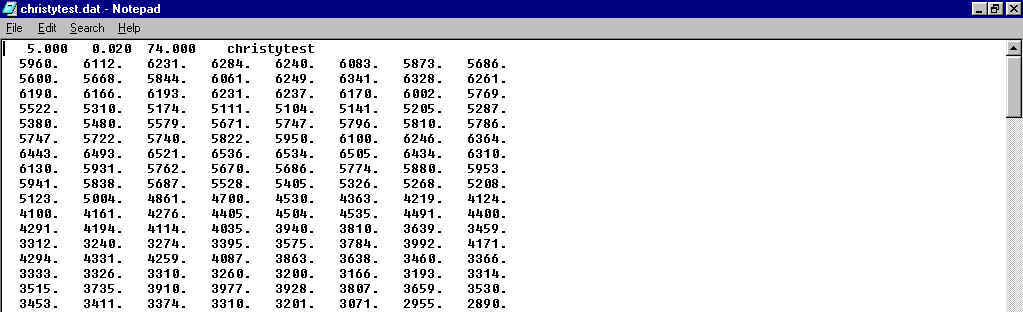
In this test example I want to use the data in a program that accepts JADE *.MDI format files. I have a header that I paste and modify as in this example:
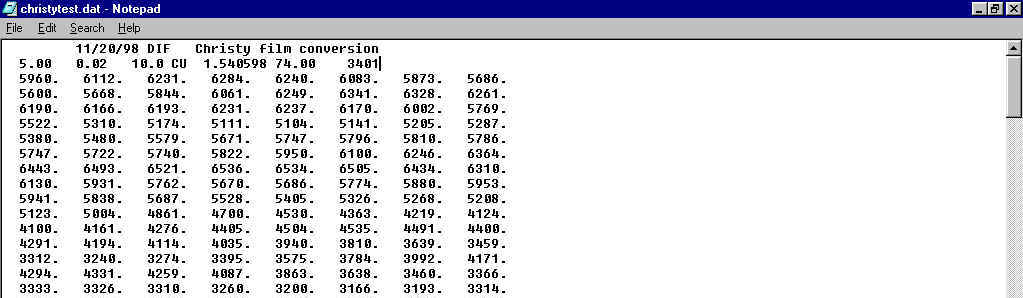
I then do a Save As and save the file as an *.MDI file:
In this example I already had a Christy.mdi file set up and simply saved it to replace the *.dat file: