Diamond 2.1: Distances, angles, and torsion angles
Diamond 2.1 Features Overview...
Previous: Handling of mixed sites...
Next: VRML export...
Diamond can calculate distances between two atoms, angles between three
atoms, and torsion angles, each with standard uncertainties, presuming that
standard uncertainties have been defined for cell or atomic parameters.
Distances and angles can be calculated for selected atom types of the current
structure and within an arbitrary distance range, and listed in a special table
right beneath the structure picture (examples below, abbreviated; the lists
have been directly copied via clipboard from the Diamond data table):
Ti 1 F 8 1.732(4) 3x
F 1 2.026(5) 3x
Ti 2 F 10 1.720(6) 1x
F 6 1.745(4) 1x
F 1 1.895(4) 1x
F 5 1.914(5) 1x
F 3 1.947(4) 1x
F 2 2.037(5) 1x
Ti 3 F 7 1.708(4) 1x
F 9 1.732(4) 1x
F 4 1.874(5) 1x
F 2 1.891(4) 1x
F 3 1.995(5) 1x
< omitted for brevity >
F 1 Ti 2 1.895(4) Ti 1 2.026(5) 147.97(21)
F 2 Ti 3 1.891(5) Ti 2 2.037(5) 148.78(25)
F 3 Ti 2 1.947(4) Ti 3 1.995(5) 151.05(22)
F 4 Ti 3 1.874(5) Ti 4 2.058(5) 143.40(24)
F 5 Ti 2 1.914(5) Ti 3 2.002(5) 152.72(22)
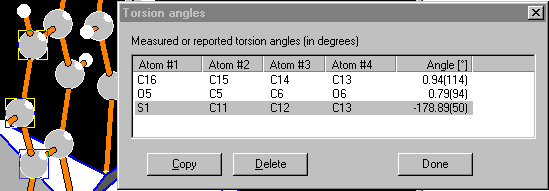
Distances, angles, and torsion angles can be measured interactively in the
structure picture by clicking two, three, or four atoms, rsp., each. The
results may be added to the internal lists of distances or angles and appear as
geometric parameters in the data sheet and the CIF export as "geom_dist_XXX"
etc. - with standard uncertainties and symmetry codes, of course.
The default settings for the colors are those used for the atom type components.
That means, if you have defined brown for the atom type "Fe+3" in the Diamond
atom type resource, all Fe+3 components on mixed sites will become brown by
default.
Diamond 2.1 Features Overview...
Previous: Handling of mixed sites...
Next: VRML export...
|


